Ultrasound Therapy
Ultrasound therapy, a non-invasive medical treatment, has become a cornerstone in the field of rehabilitation and pain management. Employing high-frequency sound waves, ultrasound therapy penetrates deep into tissues to elicit a range of therapeutic benefits.
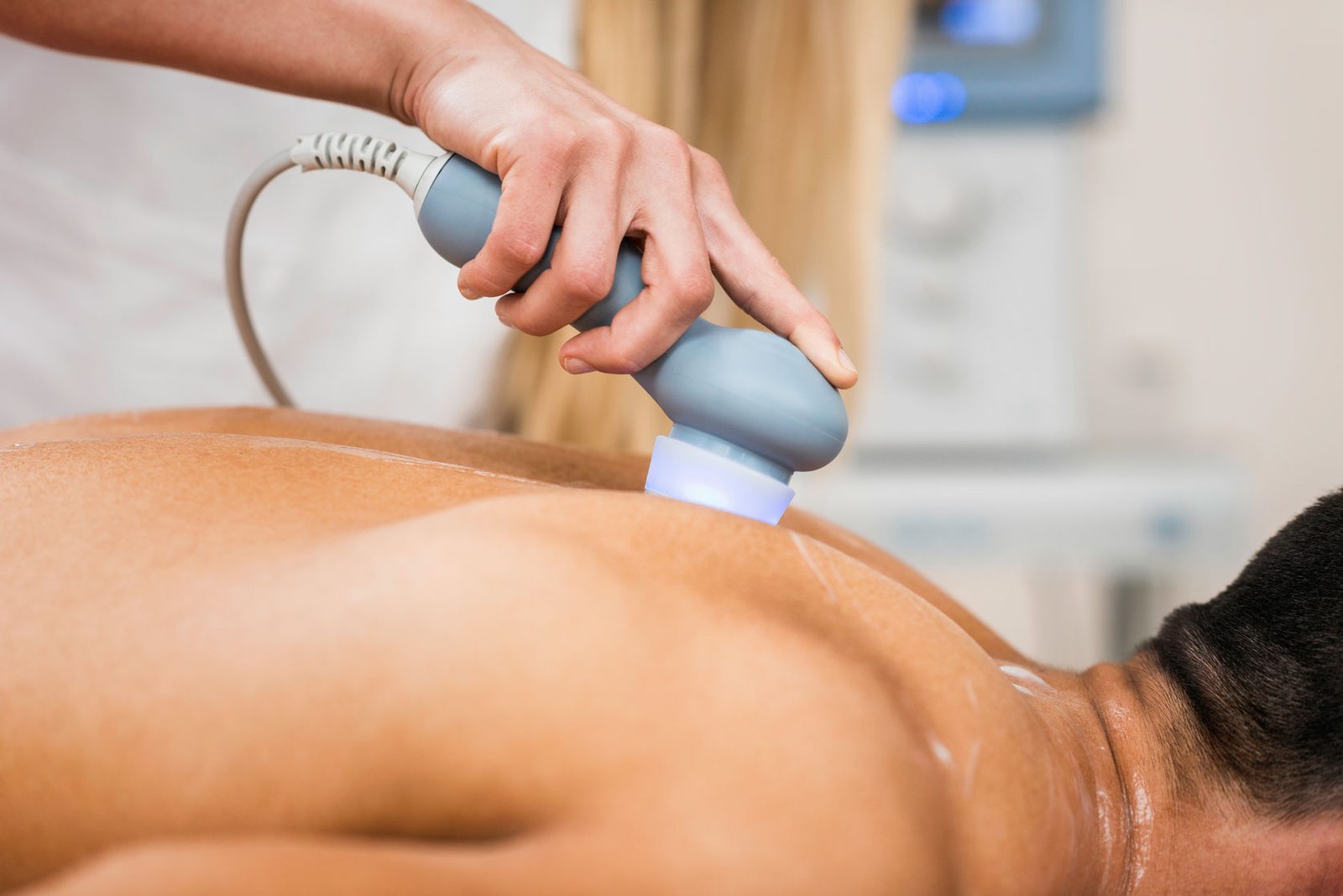
How Ultrasound Therapy Works:
During an ultrasound therapy session, a gel is applied to the skin over the targeted area to facilitate the transmission of sound waves. A handheld device known as an ultrasound transducer is then gently moved across the skin, emitting either continuous or pulsed ultrasound waves. These waves create micro-vibrations within the tissues, leading to various therapeutic effects.
Therapeutic Effects of Ultrasound Therapy :
- Pain Relief : Ultrasound therapy helps alleviate pain by stimulating the body's natural pain-relieving mechanisms. It triggers the release of endorphins while reducing inflammation and swelling, providing relief from conditions such as arthritis, tendonitis, and muscle strains.
- Tissue Healing : By enhancing blood flow to the affected area, ultrasound therapy promotes tissue healing. Increased circulation delivers vital nutrients and oxygen to injured tissues, expediting the repair process. This makes it particularly beneficial for soft tissue injuries like ligament sprains and muscle tears.
- Collagen Production : Ultrasound therapy stimulates collagen production, a crucial protein for tissue repair and regeneration. By promoting collagen synthesis, it helps strengthen weakened tissues, enhancing their resilience and functionality.
- Muscle Relaxation : Tight muscles and muscle spasms can be effectively addressed with ultrasound therapy. The increased blood flow induced by ultrasound helps relax tense muscles and alleviate spasms, improving flexibility and range of motion.
Application of Ultrasound Therapy:
Ultrasound therapy is widely utilized across various medical disciplines, including physical therapy, sports medicine, and orthopeadics. It is commonly incorporated into treatment plans for conditions such as:
- Sports Injuries : Including muscle strains, ligament sprains, and tendonitis.
- Chronic Pain : Such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and myofascial pain syndrome.
- Postoperative Rehabilitation : To aid in the recovery process and minimize scar tissue formation.
- Soft Tissue Injuries : Including bursitis, fasciitis, and contusions.