Biomechanical Correction
Biomechanical correction is a fundamental aspect of rehabilitation and physical therapy that focuses on identifying and addressing faulty movement patterns, musculoskeletal imbalances, and dysfunctional biomechanics. By analyzing movement mechanics, joint alignment, and muscle activation patterns, biomechanical correction aims to restore optimal function, reduce pain, and prevent injuries. In this guide, we'll explore the principles of biomechanical correction and practical strategies for optimizing movement patterns.
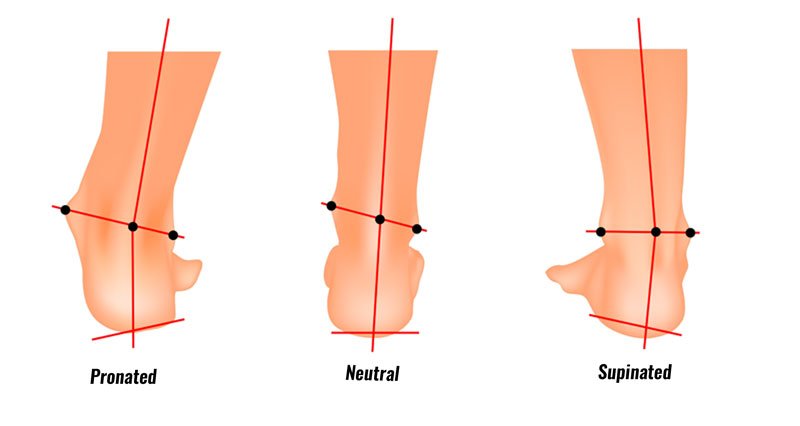
Biomechanical correction is essential for optimizing movement patterns, reducing pain, and improving function in individuals with musculoskeletal dysfunction. By addressing underlying imbalances, restoring optimal biomechanics, and promoting functional integration, biomechanical correction strategies can help individuals achieve improved movement quality, stability, and performance in daily activities and sports. Whether through manual therapy, corrective exercises, ergonomic modifications, or movement retraining, prioritizing biomechanical correction fosters a strong foundation for musculoskeletal health and overall well-being.
Principles of Biomechanical Correction:
- Movement Analysis : Biomechanical correction begins with a comprehensive assessment of movement patterns, joint mobility, and muscle function. This involves observing how an individual moves during various activities, identifying areas of dysfunction or compensation, and assessing joint range of motion and muscle strength.
- Identification of Imbalances : Biomechanical correction aims to identify musculoskeletal imbalances, asymmetries, and dysfunctional movement patterns that contribute to pain, dysfunction, or increased injury risk. Common imbalances may include muscle weakness, tightness, or poor coordination between opposing muscle groups.
- Addressing Root Causes : Biomechanical correction seeks to address the underlying causes of musculoskeletal dysfunction, rather than simply treating symptoms. This may involve addressing biomechanical faults, improving joint alignment, restoring muscle balance, and correcting movement compensations.
- Individualized Treatment : Biomechanical correction strategies are tailored to each individual's specific needs, taking into account factors such as medical history, biomechanical assessments, functional goals, and lifestyle factors. Treatment plans may include a combination of manual therapy, corrective exercises, ergonomic modifications, and movement retraining.
- Functional Integration : Biomechanical correction emphasizes functional movement patterns that translate into improved performance during daily activities, work tasks, and sports. Rehabilitation exercises and corrective strategies focus on improving movement quality, stability, and efficiency in functional tasks relevant to the individual's goals and lifestyle.
Practical Strategies for Biomechanical Correction:
- Manual Therapy Techniques : Incorporate manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilization, soft tissue mobilization, and myofascial release to address restrictions in joint mobility, reduce muscle tension, and restore optimal movement mechanics.
- Corrective Exercises : Prescribe specific exercises targeting muscle imbalances, weaknesses, or movement dysfunctions identified during movement analysis. Focus on strengthening weak muscles, stretching tight muscles, and improving neuromuscular control and coordination.
- Movement Retraining : Use movement retraining exercises and functional drills to teach proper movement patterns and reinforce optimal biomechanics. Incorporate proprioceptive feedback, balance exercises, and movement progressions to improve motor control and movement efficiency.
- Ergonomic Modifications : Make ergonomic adjustments to the individual's environment, workstation setup, and daily activities to reduce biomechanical stress and promote optimal posture and alignment. Provide recommendations for ergonomic furniture, tools, and equipment to support proper body mechanics.
- Patient Education : Educate individuals on the importance of proper biomechanics, movement awareness, and injury prevention strategies. Provide guidance on posture, body mechanics, and self-care techniques to empower individuals to take an active role in their rehabilitation and long-term musculoskeletal health.